4 tips to manage asthma symptoms
Asthma is an inflammatory disease caused by inflammation in the lungs’ airways. If statistics are to be believed, there are almost 25 million people in the country with asthma. Asthma patients are likely to be triggered by certain foods and environmental factors. However, this varies from patient to patient and depends on the severity of the condition. This article sheds light on some effective tips to help asthma patients keep their symptoms at bay.
-
- Keep these treatment options handy
The best way to manage asthma is to seek medical intervention. Fasenra® and Nucula are two excellent medications. Fasenra® is used as one of the most effective asthma treatment options. It can be self-injected using an injection pen. Fasenra® is used to improve breathing in asthma patients and lower their use of oral steroids use. It is to be taken once every eight weeks. Mepolizumab or Nucala works by reducing the number of eosinophils in the blood, thereby reducing airway inflammation. Oher clinical treatment options include Tezepelumab, Xolair, and Zyrtec.
- Keep these treatment options handy
-
- Eat and avoid these foods
Lifestyle changes like adding foods to one meal regimen and avoiding certain foods can also effectively manage asthma. Ginger should be added to daily meals because they are anti-inflammatory and can reduce asthma symptoms. Apart from this, including foods like salmon and walnuts, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, can also help strengthen the lungs, thereby keeping asthma flareups at bay. At the same time, it is necessary to be aware of foods that aggravate or worsen asthma. Some of these foods include aerated drinks, shellfish, and milk, as these can increase mucus and inflammation in the lungs, making it difficult to manage asthma.
- Eat and avoid these foods
-
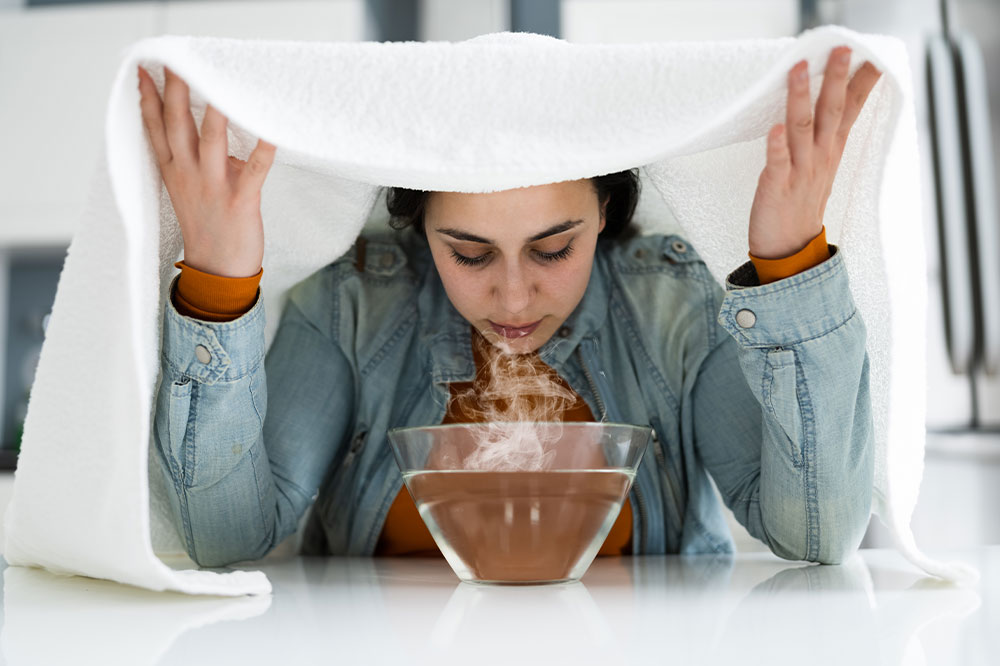
- Steam inhalation or bath
A steam inhalation or bath is one of the effective tips for managing asthma naturally. The steam helps open up airways, providing relief from symptoms like wheezing and difficulty breathing.
- Steam inhalation or bath
- Lose visceral fat
Individuals with excess visceral fat are more vulnerable to asthma, as the extra weight can press against the lungs, putting pressure on them. Losing weight can be helpful for asthma patients as it can help increase lung volume and reduce the risk of diseases like hypertension and diabetes, which also typically aggravate asthma symptoms.