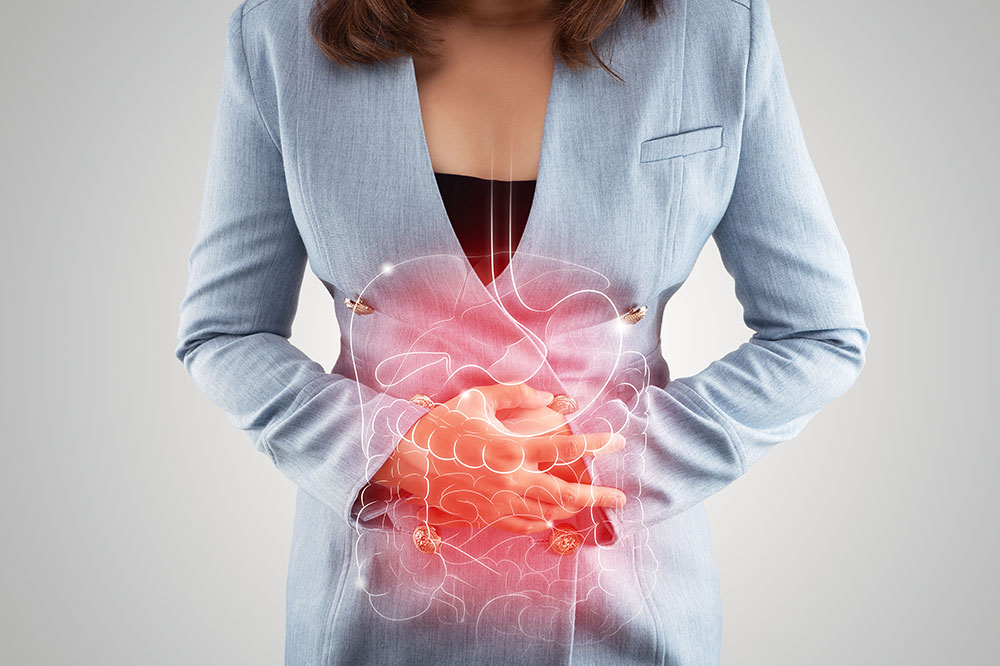
5 digestive conditions and their symptoms
Located between the small intestine and the esophagus, the stomach is the center of the digestive system. In most cases, other health disorders, the consumption of certain foods, the quantity of food consumed, and the timing of meals can upend the digestive process. This leads to the manifestation of several symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, appetite changes, belching, and abdominal pain. Each of these symptoms or combination of symptoms is the result of a specific stomach condition. Here are some of the common digestion-related stomach conditions that trouble almost everyone:
Gallstones: Formed in the gallbladder, gallstones are hard deposits of digestive fluid. The gallbladder is responsible for storing and secreting the bile required for digestion, and stones form if the gallbladder does not empty out properly. These deposits also form when there is a high amount of cholesterol or waste products in the bile. Intense pain can occur if the gallstones block the ducts that lead from the gallbladder to the intestines. Medications and surgery are usually the solutions for dissolving or removing the stones, respectively.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) : GERD occurs when the acid in the stomach flows back up the esophagus. A person experiences a burning sensation in their chest due to this. While heartburn and acid reflux are common once in a while, experiencing these symptoms for more than twice a week can indicate GERD. The symptoms of this stomach condition usually include bad breath, tooth erosion, breathing trouble, and trouble swallowing. Avoiding trigger foods and taking medications help people with mild GERD.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) : IBS causes stomach pain and discomfort, which may be experienced at least thrice a month and can go on for several months without any relief. The main cause of IBS is not yet known, and the symptoms usually include constipation, diarrhea, and bloating. The symptoms usually vary from person to person, and treatment involves diet modifications. The inclusion of probiotics and low-fat, high-fiber foods and the exclusion of trigger foods can help ease the symptoms effectively.
Ulcerative colitis : An inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis affects the colon or large intestine. Ulcers and sores begin to develop in the colon as the immune system malfunctions and considers food as an invader. This leads to urgent and frequent bowel movements, along with other symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and blood in the stool. Treatment for this stomach condition includes diet modifications, medications, and surgery.
Crohn’s disease: Similar to ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease. It usually affects the terminal ileum, which connects the colon to the small bowel. Although the main cause of Crohn’s disease is not known, family history and genetics may be common risk factors. The symptoms of this stomach condition generally include diarrhea, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, fever, and weight loss. The treatment options include surgery and medication.
Acute or chronic, it is important to consult a gastroenterologist for a proper resolution to the problem. A gastroenterologist is a trained healthcare professional who can take care of disorders and diseases relating to the digestive system. They can treat conditions like IBS, jaundice, inflammatory bowel disease, hepatitis, pancreatitis, gastro-oesophageal acid reflux, and polyps in the intestine. They are also qualified to deal with cases involving pancreatic cancer.
Certain prescription-based treatment alternatives effectively subdue the symptoms of the above-mentioned digestive conditions. For example, STELARA ® is an effective alternative to treat severely active Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis in adults over 18. Before taking such treatments, one must check their side effects and use them only after consulting a healthcare expert. Another prescription is XELJANZ®, which has been tested for both UC and Crohn’s disease, with more success observed in UC.