Common IUD side effects and how to tackle them
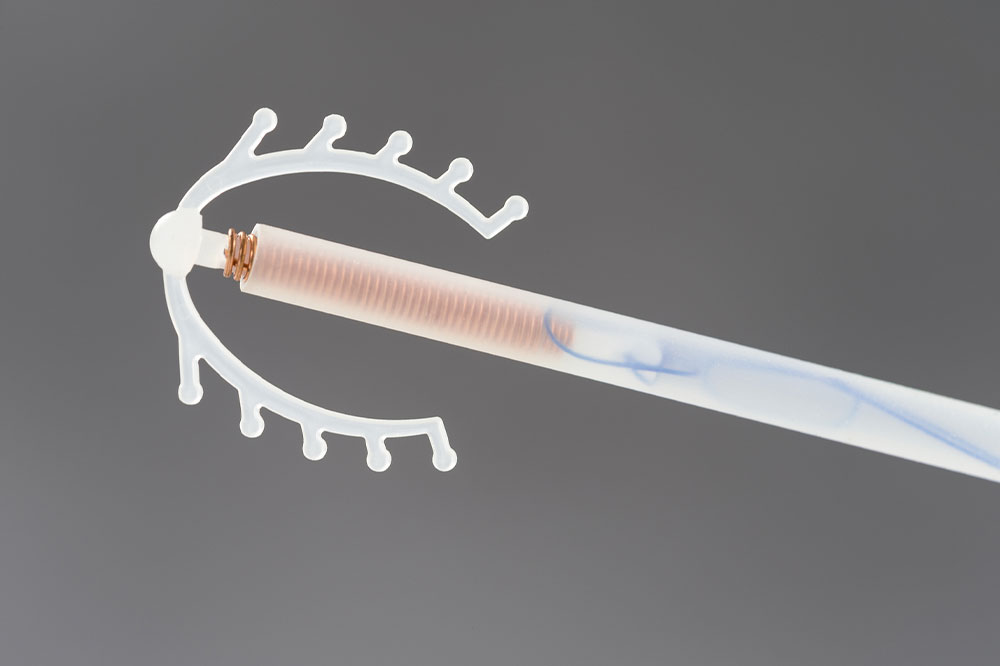
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are a popular form of birth control. Shaped like a “T,” they are inserted towards the top of a woman’s uterus to prevent sperm from reaching and fertilizing the egg. There are two forms of IUDs: hormonal and non-hormonal. Both have different side effects on different people, and users often experience them in the first few weeks of insertion. But the good news is that the side effects can be managed.
What are the side effects of IUDs?
The most common side effects are irregular bleeding for a few months, pain, cramping, dizziness, and lighter/shorter periods or no periods at all. Women may also experience premenstrual syndrome (PMS) with symptoms like headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, or skin blemishes. Other rarer side effects include cysts on the ovary and infections due to bacteria entering the cervix or uterus.
Sometimes, IUDs can shift or get displaced in the uterus, increasing the risk of embedment (or when the device attaches to the wall of the uterus), perforation (when the IUD goes through the wall of the uterus), migration (when the IUD moves to a different location in the uterus), and expulsion (when the IUD moves out of the uterus).
How to tackle the side effects?
Here are some tips on what one can do before, during, and after IUD insertion to manage side effects better:
Before the appointment
Doctors may recommend pain-reducing treatments for those worried about the pain. This is in addition to a treatment to soften the cervix an hour before the procedure. Women heading to get an IUD are also suggested to wear comfortable clothes and carry essentials like a heating pad, a panty liner or sanitary napkin, and some juice to fight any dizziness.
During the procedure
It is recommended to stay as calm as possible during the procedure, so meditation and breathing exercises may help. If requested, some doctors administer laughing gas or another pain-reducing treatment during the procedure to minimize pain further.
After insertion
Many women experience bleeding after insertion, so the sanitary napkins or panty liners brought along come in handy. The type of IUD used also determines the side effects. For instance, hormonal IUDs can lighten periods over time and help reduce cramping. On the other hand, non-hormonal IUDs may cause heavier periods and increase cramping. Since heat helps relieve cramping, one may use a heating pad after the procedure. Drinking rosehip tea can also help.
As with all menstruation-related symptoms, the IUD side effects differ from person to person. Those experiencing PMS symptoms should get sufficient rest and practice deep breathing exercises to relieve headaches and other discomforts.
It may take six to eight months for the body to adjust to an IUD fully. Besides following these tips to tackle IUD side effects, one should consult a physician if they experience fever, severe pain or cramping, bleeding during or after intercourse, unusual vaginal discharge, pregnancy symptoms, or difficulty breathing. It is also advisable to contact a doctor if one can no longer feel the strings of their IUD to ensure it has not moved.