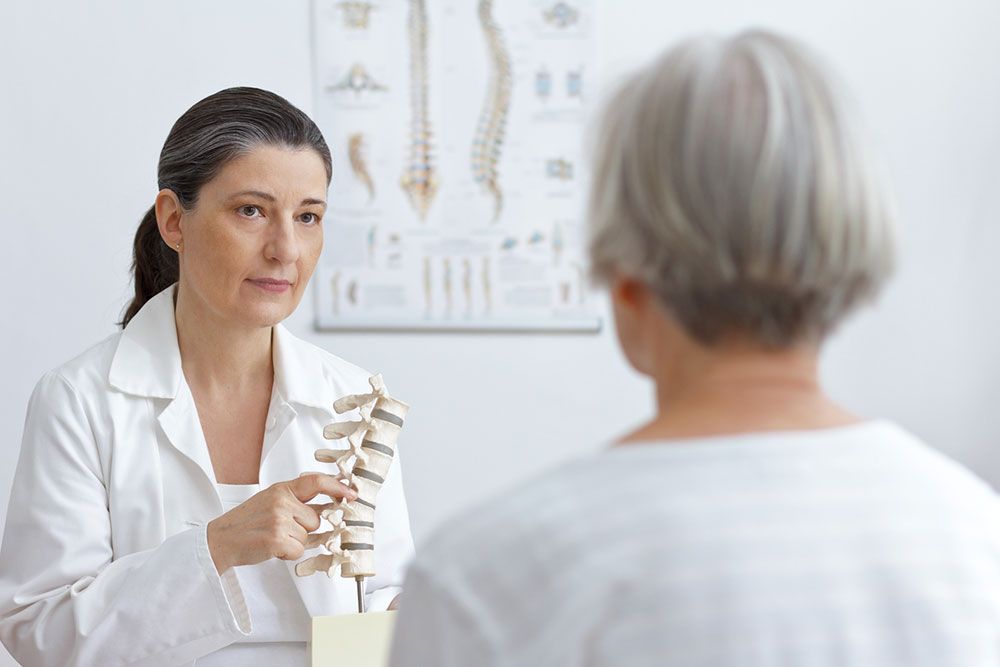
Identifying and managing spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is a rare genetic disease that causes the progressive weakening of muscles in the body. This occurs due to the loss of motor neurons, which are responsible for controlling muscle movement. Depending on when the symptoms begin to appear, this condition is categorized into four distinct types, from severe to mild. Read on to find out more about this condition, its symptoms, diagnosis, and recommended treatment plans.
Symptoms of spinal muscular atrophy
Some of the typical symptoms of this condition include:
Floppy or weak arms or legs
Mobility problems, such as difficulties in standing up or walking
Tremors or muscle twitching
A curved spine (scoliosis)
Swallowing problems
Breathing difficulties
Individuals with this condition experience progressive muscle weakness, which can also give rise to complications such as bone fractures, hip dislocation, pneumonia, respiratory infections, malnutrition, and dehydration.
Diagnosing spinal muscular atrophy
Doctors begin with a thorough physical exam along with a detailed examination of one’s healthcare history. Depending on these results, they may recommend one or more of the following:
An enzyme and protein blood test to check for levels of creatine kinase. High levels of this enzyme in the bloodstream signal deteriorating muscles.
A genetic test to identify problems with the SMN1 gene. In most states, this is now conducted routinely for newborns.
An electromyogram, or nerve conduction test, to measure the activity of muscles and nerves.
A muscle biopsy to check for any deterioration or loss.
Treating spinal muscular atrophy
There is no cure for this condition at present. In most cases, a team of doctors, such as physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, and other specialist doctors, are involved in formulating a treatment plan, which tends to focus on managing symptoms and pain. The treatment plan depends on the type and intensity of SMA and may involve the following steps:
Encouraging exercise to facilitate movement and breathing.
Using movement aids such as crutches, walkers, and wheelchairs.
Relying on feeding tubes or following a special nutrition plan.
Making use of orthopedic braces or surgery to treat bone and joint problems.
Gene replacement therapy, where a one-time IV infusion is used to replace a missing or faulty SMN1 gene with a functioning gene. This is generally recommended for children under the age of two.