Overactive bladder – Causes, symptoms, and management
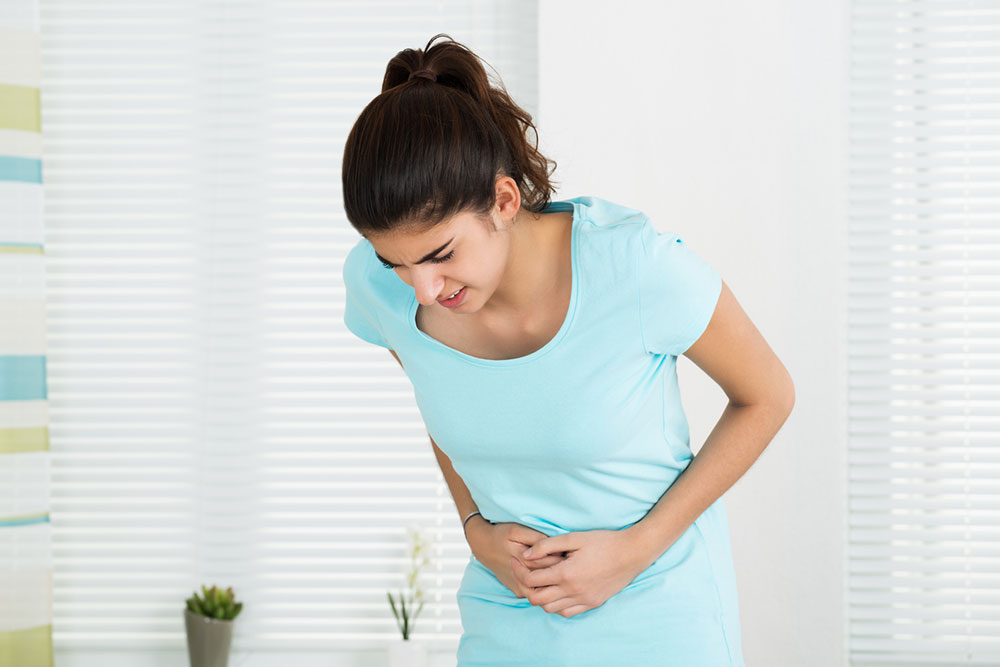
Overactive bladder, or OAB, is when one feels a persistent, uncontrollable urge to pass urine. Often, people with this disease choose to stay away from social situations because of the embarrassment involved. But the good news is that identifying this problem early on can help treat it on time and prevent it from escalating. Doctors usually suggest a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle changes. Here is everything one should know about OAB:
Causes and triggers of overactive bladder
– Diabetes
High blood sugar can damage the urinary tract nerves, which culminates in bladder problems. So, people with diabetes are highly prone to overactive bladder.
– Neurological disorders
Often, loss of control over urination can happen because of an underlying nerve, brain, or spinal cord problem. People with disorders like Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis may suffer nerve damage, which can cause or worsen OAB.
– Bladder stones
Bladder stones or tumors and infections of the bladder can increase one’s risk of OAB because the bladder’s normal functioning is severely affected in many of these cases.
– Certain treatments
Sometimes, treatments for certain other diseases may trigger an overactive bladder, a side effect of the intervention.
Symptoms of overactive bladder
– Urgency incontinence
Urgency incontinence is when one feels a sudden urge to urinate, after which one may experience an involuntary urine leak.
– Loss of sleep
The sudden urge to pass urine at night may cause severe sleep disturbances. That’s why many doctors suggest sleeping on the side and avoiding too many fluids just before bedtime.
– Loss of appetite
People with OAB are usually fatigued because of the number of times they need to rush to the washroom, and this fatigue may lead to loss of appetite.
– Bladder spasms
Sometimes, OAB patients may experience cramps or pain in their lower abdomen and an urge to pass urine simultaneously.
Treatment options
– Biofeedback
In this treatment method, the patient is connected to electrical signals, which receive information about what is happening inside the body. Then, the sensors help one make specific conscious changes, such as strengthening the pelvic floor muscles, to manage and control urination.
– Kegel exercises
Kegel or pelvic floor muscle exercises strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and urinary sphincter. Following these exercises can help one control involuntary contractions of the bladder.
– Bladder training
Patients practice delaying their urge when they need to go to the bathroom. These delays are initially for half an hour, but the duration gradually increases to help one gain better control over one’s bladder.
– Use of a catheter
Sometimes, if a person is unable to empty their bladder properly, doctors may recommend the use of a catheter to clear the bladder. However, this procedure should only be performed on a doctor’s recommendation.